7 C’s of SEO: A Complete Framework for Ranking and Revenue

Tags:7 C’s of SEO
Written By

Bikash Yadav
SEO EXPERT
SEO Expert & Digital Marketing Strategist with 8+ years of experience helping businesses grow online. Read more



Search engines (like Google) are like treasure-hunters seeking the best sites. SEO is how we map our site so search engines and people find it.
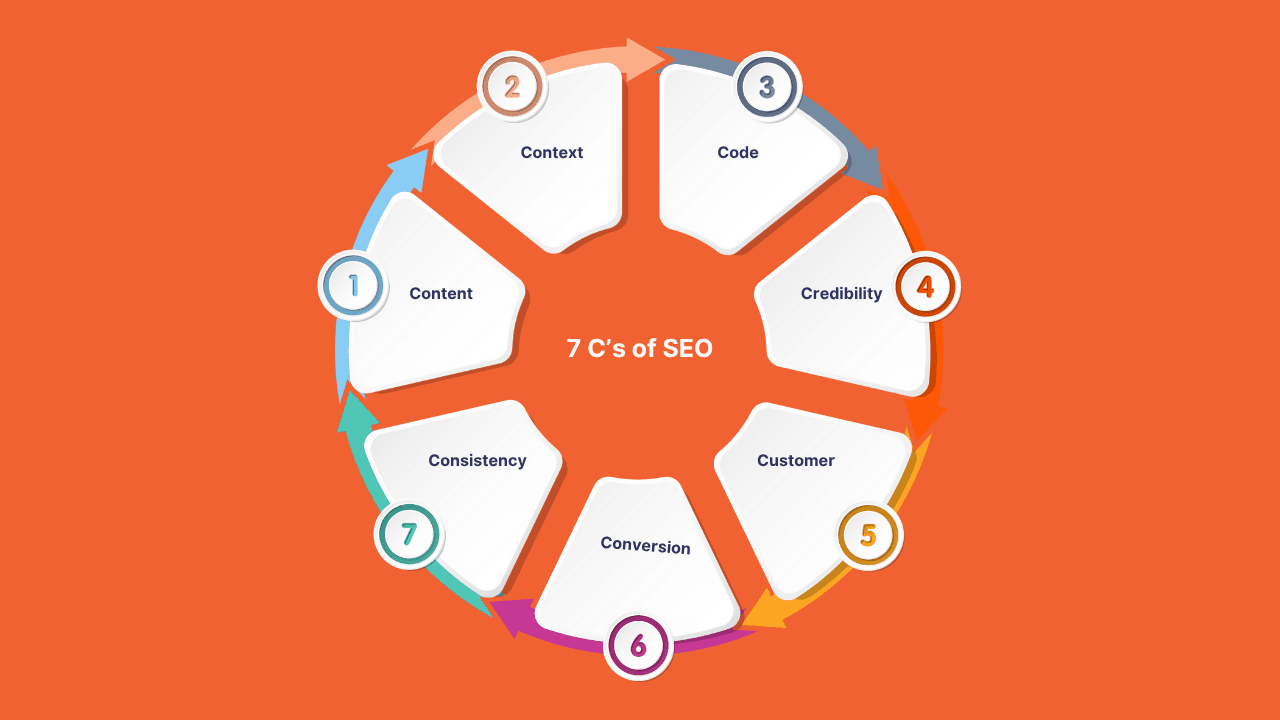
One way to remember the key parts of SEO is the “7 C’s”: Content, Context, Code, Credibility, Customer, Conversion, and Consistency.
Each C is like a rule in our treasure map. I’ll explain each C in simple terms but with enough detail that you will still learn something new.
We’ll also use tools and real stats to make our points trustworthy. Ready to dig in? Let’s start!
Imagine SEO as building a skyscraper. First, you need a solid foundation for search engines to crawl (like strong crawlability), then brick after brick of quality content, and a roof of authority.
In one infographic example, the first three C’s of SEO are Crawlability (search engines must easily “get inside” your site), Credibility (others must vouch for you), and Content (what you actually show visitors). We’ll focus on our 7 C’s, starting with Content.
User satisfaction = SEO Success
Think of content as the stories, pictures, and videos in your site’s library. Good content means you’ve written or shown something that people really want or need.
It’s not enough to just write a blog post; the post must be useful and easy to understand.
The famous SEO expert Brian Dean says “Quality Content” is the most important SEO factor:
Google wants to show users “high-quality, informative, and relevant content.”. In other words, Google’s treasure-hunters reward sites that give people the answers they seek.
Have you ever clicked on a search result only to find the page didn’t help? Google hates that. So your content must truly help your audience.
HubSpot study found 70% of marketers report that content marketing grows their leads and engagement, and content-focused sites can get about 7.8× more traffic than competitors who neglect content. This tells us: great content pays off.
Tools & Tips:
Use tools like Google Trends, AnswerThePublic, or Ahrefs Content Explorer to research what topics people care about. If you’re writing a piece, imagine explaining the topic to a friend: make it clear, use short sentences, and include relevant keywords naturally.
Tools like Grammarly or Yoast SEO can check your writing quality. Break up text with subheadings and lists so it’s easy to scan. for example:
Every new paragraph should keep the reader’s interest. Ask yourself: “Would this be interesting if you were reading it?” If not, make it interesting.
By creating useful and engaging content, you make Google’s job easy, and Google, in return, will reward you with page rank.
Context means making sure your content fits why someone is searching. Every search has an intent – a goal. People usually search to learn something, find a place, compare products, or buy something.
SEO experts call these “informational, navigational, commercial, or transactional” queries. For example, if someone searches “buy toy car”, their intent is clearly to purchase. They want links to stores, not a blog about toy history.
Do you know why your article ranks? It’s not just content quality; it must also satisfy the searcher’s intent. Brian Dean explains that satisfying search intent is Google’s #1 goal.
In fact, he notes that 99% of all search queries fall into those 4 intent categories. If your content doesn’t match the intent behind the query, you’ll lose the game no matter how long or detailed it is.
Tools & Tips: To nail context:
Ask yourself: “Would a kid find this page useful for what they want?” If yes, you’ve likely matched intent.
For SEO experts, we always say: write for people first, then polish for search. But remember, those people have a purpose behind their visit – your context must match it.
Code is the engine and wiring hidden behind your website. Just like an electric toy needs a good battery and circuits to run, your site needs clean, fast code.
Technical SEO includes things like page speed, mobile-friendliness, and crawlability (letting search bots read your pages easily).
Think: would you stay on a website that took ages to load or had buttons that don’t work? Most people (and Google) won’t.
For example, Google data shows 47% of visitors expect a page to load in 2 seconds or less, and 40% will abandon a page that takes longer than 3 seconds.
In fact, if your page goes from 1 second load time to 3 seconds, the probability that visitors bounce (leave immediately) jumps by 32%. Those are huge losses! So speed is not optional.
On the right, an infographic illustrates key SEO code factors and clear calls-to-action. It reminds us that broken code (or lack of a CTA) can drive visitors away.
What to do (tools & tips):
By tightening your code, you speed up the site and make sure both users and search engines can use it easily. Remember: fast, mobile-ready code = happier visitors and better rankings.
Building trust with both users and search engines is crucial. Credibility comes from earning quality backlinks from authoritative sites, maintaining accurate information, showcasing expertise through author bios, and collecting positive reviews.
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) has become a critical Google ranking factor, especially for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics.
In SEO terms, that means backlinks (other sites linking to yours), positive reviews, and recognized authority.
Google famously treats each high-quality backlink as a vote of confidence. The more (and better) votes you have, the more Google will trust and rank your site.
But backlinks aren’t the whole story. Think of reviews and testimonials as modern word-of-mouth.
Studies show that 90% of consumers read online reviews before visiting a business, and 88% of consumers trust those reviews as much as personal recommendations.
That means having good ratings and comments (even on Google My Business, Yelp, Facebook, etc.) boosts your credibility not just with people, but with search engines too.
Tools & Tips:
High credibility pays off. For instance, having a more authoritative domain and backlinks typically correlates with higher rankings.
And since almost 9 in 10 people trust online reviews as much as friends’ advice, don’t underestimate the power of making customers happy and vocal.
Put yourself in their shoes: imagine you’ve designed the perfect site for customers. What makes it work? Clean navigation, friendly design, and content that feels like it was made just for them.
The Customer C is about knowing who your visitors are and what they like, then tailoring the experience to those needs. In adult terms, we call this user experience (UX) and personalization.
Ask yourself: “Who is coming to my site? What do they want?” SEO experts dive into analytics and user data to answer these questions.
For example, one stat shows that 70% of people prefer to search for brand info on mobile devices – that’s a clue that for many businesses, half the audience might be on phones most of the time.
If your mobile site is clunky, you’ve lost them. Other times, maybe your audience skews older and values simple text over flashy graphics – you adjust accordingly.
Tools & Tips:
When your audience feels understood, they stay longer, click more links, and come back. If not, questions like “Why did you leave?” or tools like Hotjar will give clues.
Ultimately, traffic without conversions is meaningless: buy a product, sign up for a newsletter, or contact you. That “something” is your conversion goal.
The Conversion C focuses on making this as easy and clear as possible. In real life, think of conversion like a friendly salesperson in a store who guides a customer: your site needs clear signs and buttons so visitors know what to do next.
Look at this stat: over 1 in 3 marketing leaders name conversion rates as a top success metric. Yet, nearly two-thirds of marketers see their landing pages convert below 10%. That gap means we have to optimize carefully.
Tools & Tips:
A helpful trick is to ask yourself, “If I were a first-time visitor, would I know what to do on this page?” If the answer isn’t a clear “Yes!”, adjust the layout or text.
Remember, the journey should feel smooth. You want your site to be like a friendly helper, not a confusing maze.
Imagine you planted a garden and only watered it once. It would wither. Consistency in SEO means regularly tending your site with fresh content, updates, and maintenance. Search engines favor sites that stay active and up-to-date.
For example, fresh content signals (especially for news or fast-changing topics) can boost your visibility.
That doesn’t mean every page needs daily changes, but you should have a steady rhythm. Maybe one new blog post a week, or updating old articles with new data every few months. Consistent activity tells Google your site is alive and relevant.
Tools & Tips:
By being consistent – like watering that garden – your SEO efforts grow stronger over time. As one expert puts it, search engines often view “fresh content as more reliable and relevant”. So set a schedule and stick to it.
The 7 C’s work as a team. Content without the right context or code is wasted. Trust and conversions mean nothing if your site’s inconsistent. Together, these principles create a robust SEO strategy.
Question for you: Which “C” will you tackle first to improve your site? Whether it’s writing that long-overdue blog post (Content), making your site mobile-friendly (Code), or lining up some great testimonials (Credibility) – start there. Check back on those stats and tips to guide your work.
And remember: SEO is a journey. Keep learning, keep updating, and use the tools and tactics above to help along the way. You got this.